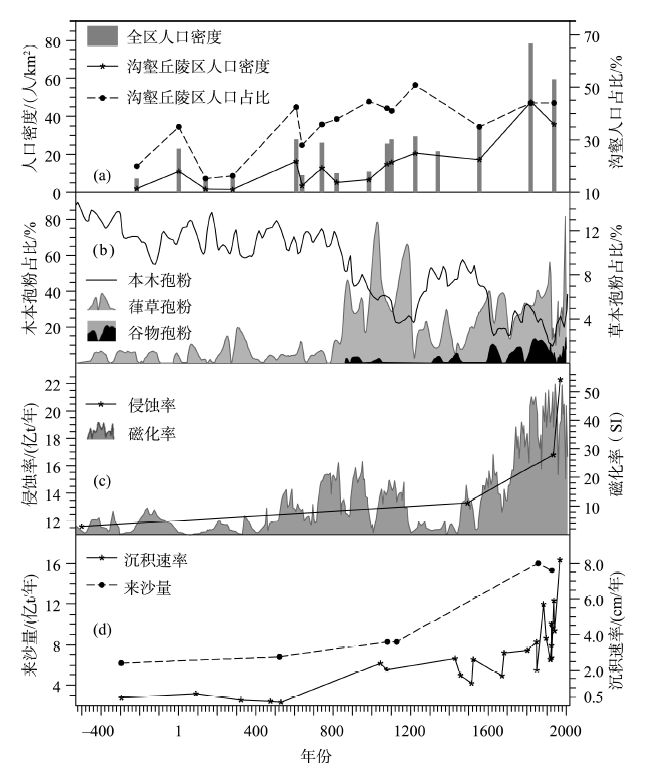
Figure 4. Changes of reclamation intensity, soil erosion in the middle reaches, and sediment load and sedimentation rates in the lower reaches of the Yellow River for the past 2500 years.
(a) Population density of the whole Loess Plateau (gray bar), as well as population density (star-solid line) and population percentage of its mid-hill gully region (dot-dash line)[60]. (b) Pollen records in alpine lake sediments in the Upper Reaches of the Weihe River, in which the decreasing of tree pollen (solid line) indicates great impact of reclamation on natural vegetation, and the increasing Humulus-type (gray shading) and Cereal-type pollen (black shading) indicate large reclamation intensity[77]. (c) Erosion rates (star-solid line) of the Loess Plateau[7,15] and magnetic susceptibility (gray shading) of the alpine lake sediments (high values indicate great erosion intensity) in the Upper Reaches of the Weihe River[78] in different periods. (d) The mean of annual sediment load[79] (dot-dash line) and sedimentation rates[80] (star-solid line) in the Lower Reaches of the Yellow River in different periods
|